Blepharitis
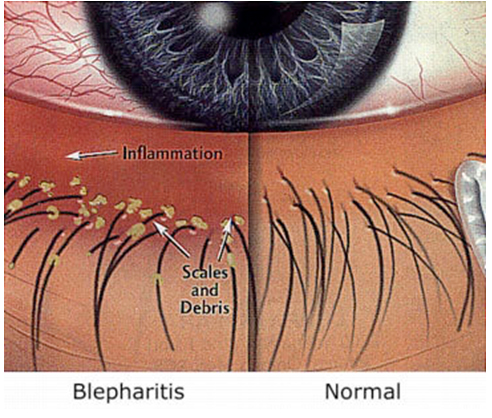
Blepharitis means inflammation of the eyelids. It usually affects the edges (margins) of the eyelids. It is not usually serious, but may become an uncomfortable, irritating, chronic condition that affects both eyes. It is often a persistent condition without an easy cure, however symptoms can usually be eased. Symptoms of blepharitis include dryness, redness, irritation, gritty sensation, and crusting of the lids. Blepharitis tends to ‘flare-up’ for a time and then ease off in severity.
Blepharitis affects the tiny meibomian glands in the eyelids lie just behind the eyelashes. You have about 25-30 meibomian glands on each upper and lower eyelid. They make a small amount of oily fluid, which comes out on the back of the eyelids next to the eye. This oily fluid forms the outer layer of the tear film, which helps smooth the tear layer over the surface of the eye and prevents the watery layer of tears from evaporating. People with blepharitis are thought to have a problem with their meibomian glands and the fluid they produce.
Co-existing conditions include dry eye syndrome (hyperlink), hordeola (styes), chalazia, and rosacea.
Treatment may include eye drops, eyelid hygiene, antibiotics and treatment of co-existing conditions if necessary. However, there is no easy cure, as the inflammation tends to recur if you do not keep up with treatment. However, with regular treatment, symptoms can usually be eased and then kept to a minimum and prevented from flaring up.



